Lecture 11.1
Unions and Collective Bargaining
Emmanuel Teitelbaum
What do Unions Do?
What is a Labor (Trade) Union?
An organization of workers who coordinate to improve their terms and conditions of employment
Areas of coordination
- Wages and benefits
- Working conditions
- Safety standards
- Rules governing termination and promotion
Collective bargaining
Strategic withdrawal of labor (strikes)
Trade Union Presence
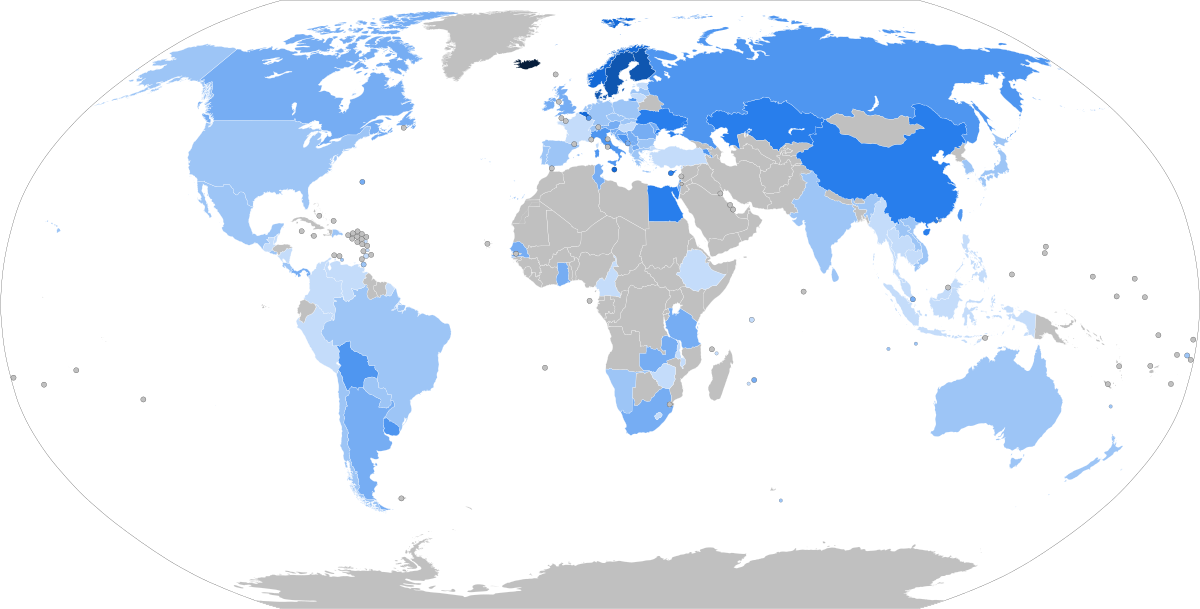
Source: ILO, retrieved from Wikimedia Commons
Workplace Democracy
- Workers’ councils
- Codetermination
- Representation on company boards
- Parity of ownership
- Worker ownership of means of production
- e.g. socialism
- Muncipal socialism
- Industrial unionism (Eugene Debbs)
Trade Union Philosophies
How did the leader you selected view unionism?
- What was its broader purposes?
- What goals would it achieve?
- Did the bio change your understanding of unions?
Union Organizing in America
A Paradox
- Unions bring many benefits
- 71% of Americans approve of unions (Gallop)
- But only 10% belong
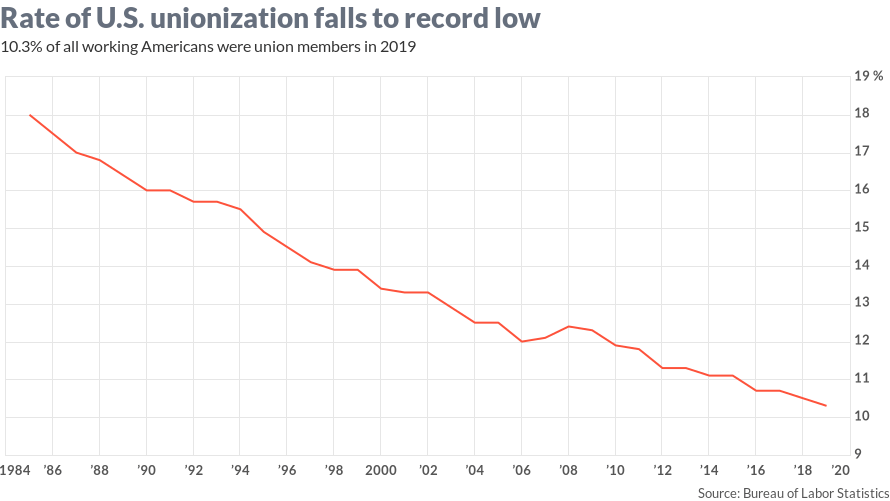
Why is Union Organizing so Hard?
Discussion
- How to improve unions?
- More effective response to globalization, automation
- Internal governance/democracy
- Success at organizing
- What kind of role should unions have?
- In economic governance
- In politics
- In society